
Finite Element Analysis - Engineering Design Tool
Finite Element Analysis - Engineering Design Tool
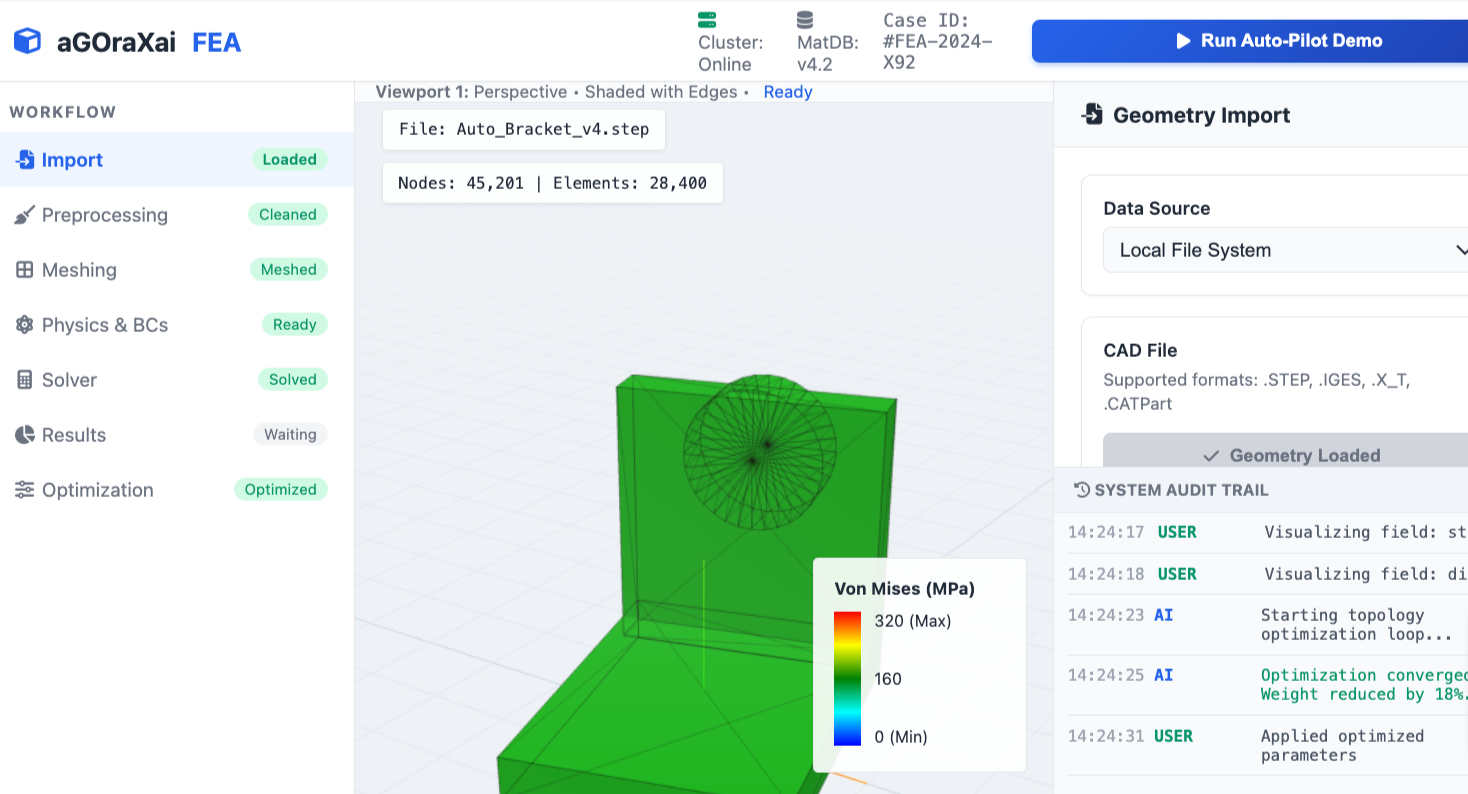
aGOraXai engineers designed a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) engineering design tool that enables seamless human collaboration with multiple AI models simultaneously. The tool integrates best-practice FEA workflows, automated AI-assisted setup, and human-in-the-loop decision points to accelerate simulation-driven design.
Key features
Multi-model AI orchestration: Coordinates multiple AI models for meshing, materials estimation, boundary-condition suggestions, solver selection, and result interpretation. Models communicate via a shared task graph so outputs are consistent and traceable.
Human-in-the-loop controls: Engineers retain control at critical steps (geometry cleanup, mesh density targets, load definitions, safety factors) with suggested actions from AI agents and easy overrides.
Automated preprocessing: Geometry defeaturing, contact detection, and adaptive meshing suggestions reduce manual setup time while preserving engineer intent.
Solver flexibility: Supports implicit and explicit solvers, linear and nonlinear analyses, static, modal, thermal, and transient dynamic simulations. Solver parameters are recommended by AI based on problem class and desired accuracy/performance tradeoffs.
Finite Element Analysis - Engineering Design Tool
aGOraXai engineers designed a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) engineering design tool that enables seamless human collaboration with multiple AI models simultaneously. The tool integrates best-practice FEA workflows, automated AI-assisted setup, and human-in-the-loop decision points to accelerate simulation-driven design.
Key features
Multi-model AI orchestration: Coordinates multiple AI models for meshing, materials estimation, boundary-condition suggestions, solver selection, and result interpretation. Models communicate via a shared task graph so outputs are consistent and traceable.
Human-in-the-loop controls: Engineers retain control at critical steps (geometry cleanup, mesh density targets, load definitions, safety factors) with suggested actions from AI agents and easy overrides.
Automated preprocessing: Geometry defeaturing, contact detection, and adaptive meshing suggestions reduce manual setup time while preserving engineer intent.
Solver flexibility: Supports implicit and explicit solvers, linear and nonlinear analyses, static, modal, thermal, and transient dynamic simulations. Solver parameters are recommended by AI based on problem class and desired accuracy/performance tradeoffs.
Material and manufacturing-aware models: AI suggests material models (elastic, plastic, hyperelastic, viscoelastic) and manufacturing constraints (residual stresses, anisotropy from additive manufacturing) using a curated materials database.
Adaptive error control and convergence guidance: AI agents monitor residuals, recommend mesh refinement zones, timestep adjustments, and preconditioning strategies to reach convergence efficiently.
Result interpretation assistants: Natural-language summaries, annotated visualizations, and automated failure-mode identification help translate simulation outputs into actionable engineering insights.
Design optimization loop: Integrates gradient-based and gradient-free optimizers with AI-guided parameterization, sensitivity analysis, and tradeoff visualizations for weight, cost, and performance.
Collaboration and traceability: Versioned simulation cases, audit trails for AI recommendations, and role-based approvals support regulatory compliance and team workflows.
Deployment and integration: Runs on local workstations, private clusters, or cloud infrastructure; provides APIs for CAD tools, PLM systems, and test data ingestion.
Benefits
Faster setup and turnaround: AI-assisted preprocessing and solver selection cut simulation setup and solve times.
Improved engineering productivity: Reduced manual tasks let engineers focus on interpretation, design decisions, and verification.
Better-informed decisions: Combined AI suggestions and engineer oversight reduce human error and broaden design exploration.
Scalable workflows: From one-off prototypes to high-throughput design studies, the tool adapts across project scales.
Typical workflow
Import CAD geometry or sketch within the tool.
AI-led geometry cleanup and defeaturing with user review and approval.
AI suggests meshing strategy and material models; engineer modifies as needed.
Define loads, constraints, and contacts with AI-proposed options and human confirmation.
Select solver and run simulation; AI monitors convergence and adjusts parameters if authorized.
Review automated results summary, annotated plots, and failure-mode flags; iterate or send to optimization loop.
Export reports, datasets, and a complete audit trail for review or certification.
Use cases
Structural component design and validation
Thermal management and heat transfer studies
Crashworthiness and impact simulations
Fatigue life prediction and durability analysis
Additive manufacturing process simulation and distortion prediction
Multiphysics problems coupling fluid, thermal, and structural analyses
Safety, ethics, and validation
Recommendation provenance: The tool logs AI-suggested actions with confidence metrics and source model identifiers so engineers can assess reliability.
Human accountability: Final design decisions remain with licensed engineers; AI outputs are treated as advisory unless explicitly certified.
Continuous validation: Models are periodically retrained and benchmarked against experimental data and industry-standard test cases.
Data governance: Supports secure data handling, access controls, and anonymization for shared datasets.
Conclusion aGOraXai’s FEA engineering design tool combines multiple AI models with human expertise to streamline simulation workflows, increase design throughput, and improve decision quality while preserving traceability and engineer control.
Finite Element Analysis - Engineering Design Tool
aGOraXai engineers designed a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) engineering design tool that enables seamless human collaboration with multiple AI models simultaneously. The tool integrates best-practice FEA workflows, automated AI-assisted setup, and human-in-the-loop decision points to accelerate simulation-driven design.
Key features
Multi-model AI orchestration: Coordinates multiple AI models for meshing, materials estimation, boundary-condition suggestions, solver selection, and result interpretation. Models communicate via a shared task graph so outputs are consistent and traceable.
Human-in-the-loop controls: Engineers retain control at critical steps (geometry cleanup, mesh density targets, load definitions, safety factors) with suggested actions from AI agents and easy overrides.
Automated preprocessing: Geometry defeaturing, contact detection, and adaptive meshing suggestions reduce manual setup time while preserving engineer intent.
Solver flexibility: Supports implicit and explicit solvers, linear and nonlinear analyses, static, modal, thermal, and transient dynamic simulations. Solver parameters are recommended by AI based on problem class and desired accuracy/performance tradeoffs.
Finite Element Analysis - Engineering Design Tool
aGOraXai engineers designed a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) engineering design tool that enables seamless human collaboration with multiple AI models simultaneously. The tool integrates best-practice FEA workflows, automated AI-assisted setup, and human-in-the-loop decision points to accelerate simulation-driven design.
Key features
Multi-model AI orchestration: Coordinates multiple AI models for meshing, materials estimation, boundary-condition suggestions, solver selection, and result interpretation. Models communicate via a shared task graph so outputs are consistent and traceable.
Human-in-the-loop controls: Engineers retain control at critical steps (geometry cleanup, mesh density targets, load definitions, safety factors) with suggested actions from AI agents and easy overrides.
Automated preprocessing: Geometry defeaturing, contact detection, and adaptive meshing suggestions reduce manual setup time while preserving engineer intent.
Solver flexibility: Supports implicit and explicit solvers, linear and nonlinear analyses, static, modal, thermal, and transient dynamic simulations. Solver parameters are recommended by AI based on problem class and desired accuracy/performance tradeoffs.
Material and manufacturing-aware models: AI suggests material models (elastic, plastic, hyperelastic, viscoelastic) and manufacturing constraints (residual stresses, anisotropy from additive manufacturing) using a curated materials database.
Adaptive error control and convergence guidance: AI agents monitor residuals, recommend mesh refinement zones, timestep adjustments, and preconditioning strategies to reach convergence efficiently.
Result interpretation assistants: Natural-language summaries, annotated visualizations, and automated failure-mode identification help translate simulation outputs into actionable engineering insights.
Design optimization loop: Integrates gradient-based and gradient-free optimizers with AI-guided parameterization, sensitivity analysis, and tradeoff visualizations for weight, cost, and performance.
Collaboration and traceability: Versioned simulation cases, audit trails for AI recommendations, and role-based approvals support regulatory compliance and team workflows.
Deployment and integration: Runs on local workstations, private clusters, or cloud infrastructure; provides APIs for CAD tools, PLM systems, and test data ingestion.
Benefits
Faster setup and turnaround: AI-assisted preprocessing and solver selection cut simulation setup and solve times.
Improved engineering productivity: Reduced manual tasks let engineers focus on interpretation, design decisions, and verification.
Better-informed decisions: Combined AI suggestions and engineer oversight reduce human error and broaden design exploration.
Scalable workflows: From one-off prototypes to high-throughput design studies, the tool adapts across project scales.
Typical workflow
Import CAD geometry or sketch within the tool.
AI-led geometry cleanup and defeaturing with user review and approval.
AI suggests meshing strategy and material models; engineer modifies as needed.
Define loads, constraints, and contacts with AI-proposed options and human confirmation.
Select solver and run simulation; AI monitors convergence and adjusts parameters if authorized.
Review automated results summary, annotated plots, and failure-mode flags; iterate or send to optimization loop.
Export reports, datasets, and a complete audit trail for review or certification.
Use cases
Structural component design and validation
Thermal management and heat transfer studies
Crashworthiness and impact simulations
Fatigue life prediction and durability analysis
Additive manufacturing process simulation and distortion prediction
Multiphysics problems coupling fluid, thermal, and structural analyses
Safety, ethics, and validation
Recommendation provenance: The tool logs AI-suggested actions with confidence metrics and source model identifiers so engineers can assess reliability.
Human accountability: Final design decisions remain with licensed engineers; AI outputs are treated as advisory unless explicitly certified.
Continuous validation: Models are periodically retrained and benchmarked against experimental data and industry-standard test cases.
Data governance: Supports secure data handling, access controls, and anonymization for shared datasets.
Conclusion aGOraXai’s FEA engineering design tool combines multiple AI models with human expertise to streamline simulation workflows, increase design throughput, and improve decision quality while preserving traceability and engineer control.

